Tel: 0086 21 32553195
0086 21 32553197
0086 21 62112950
Fax: 0086 21 60851331
0086 21 52912097
E-mail: info@agromdc.com
|
|
|
Products |
| Common Name |
Cyhalofop-butyl |
CAS NO. |
122008–85–9 |
| Chemical Formula |
C20H20FNO4 |
Molecular Mass |
357.4 |
| Structural Formula |
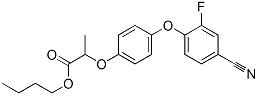 |
| Mode of Action |
Fatty acid synthesis inhibitor, by inhibition of acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACCase). Selectivity between susceptible grasses and dicotyledonous plants is attributed to the forms of ACCase present and their compartmentalisation within plant cells. Susceptible grasses contain the susceptible eukaryotic form of ACCase; dicotyledonous plants contain both susceptible eukaryotic and herbicide-resistant prokaryotic forms of ACCase, rendering them resistant to cyhalofop-butyl. Rice tolerance to cyhalofop-butyl is due to rapid metabolism to the herbicidally inactive diacid (DT50 <10 h), whereas susceptible grasses metabolise cyhalofop-butyl to the herbicidally active monoacid. Post-emergence herbicide with foliar uptake only and no soil activity. A systemic herbicide that is readily absorbed by plant tissue, is moderately phloem-mobile and accumulates in meristematic regions. Grass ****s cease growth immediately after treatment, with yellow patches appearing within 2–3 days to one week, leading to necrosis and death of the whole plant within 2 to 3 weeks. |
| Uses |
For post-emergence control of grass ****s in rice. Applied at 75–100 g/ha in tropical rice and 180–310 g/ha in temperate rice. For selectivity in Poaceae species, see M. Ito et al., J. Weed Sci. & Tech., 1998, 43(2), 122–128. |
Note:Other formulations are available on request.
|
|
